Bipolar Disorder: Symptoms, treatment, and causes

Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar Disorder is a Psychiatric condition that involves severe mood changes, from manic or hypomanic to depressive. Symptoms may differ according to the person and type of bipolar disorder.
Types of Bipolar Disorder
- Bipolar I Disorder: Involves a minimum of one manic episode, typically with the presence of depressive episodes.
- Bipolar II Disorder: Involves at least one major depressive episode4 and one hypomanic episode.
- Cyclothymic Disorder: Alternating periods of hypomanic and depressive symptoms lasting for two years or more.
Table of Contents
Cause of Bipolar Disorder
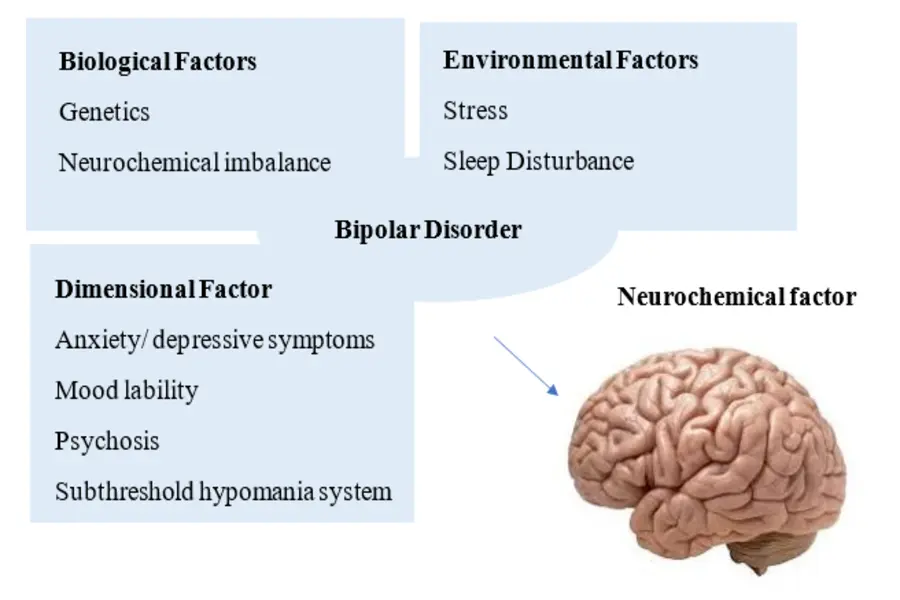
The reason for bipolar disorder is not entirely clear, but a number of factors could lead to its development:
Biological Factors:
- Genetics: There is a strong family history component, and the person is more likely to develop the illness if they have a first-degree relative with Bipolar disorder.
- Neurochemical imbalance: Imbalance of neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine could be responsible for swings in mood.
Environmental Factors:
- Stress: Traumatic experiences, major life changes, or long-term stress can include episodes.
- Sleep disturbances: Interference with sleep patterns may lead to mood instability.
Dimensional Factors:
- Anxiety/depressive symptoms
- Mood lability
- Psychosis
- Sleep problems
- Subthreshold hypomania system
Neurochemical Factor:
Brain Structure and Function:
Brain emotional processing centres are complex and multi-faceted. Amygdala, prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, and anterior cingulate cortex regulate emotional processing.
Best sellers
-
Modavinil 200mg (Modafinil)
$69.00 – $395.00Price range: $69.00 through $395.00Shop Now This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Modafil Md 200 mg (Modafinil)
$69.00 – $345.00Price range: $69.00 through $345.00Shop Now This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Modvigil 200mg (Modafinil)
$65.00 – $395.00Price range: $65.00 through $395.00Shop Now This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Vilafinil 200 mg (Modafinil)
$69.00 – $395.00Price range: $69.00 through $395.00Shop Now This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Modalert 200 mg (Modafinil)
$69.00 – $449.00Price range: $69.00 through $449.00Shop Now This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Modafresh 200 mg (Modafinil)
$65.00 – $329.00Price range: $65.00 through $329.00Shop Now This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
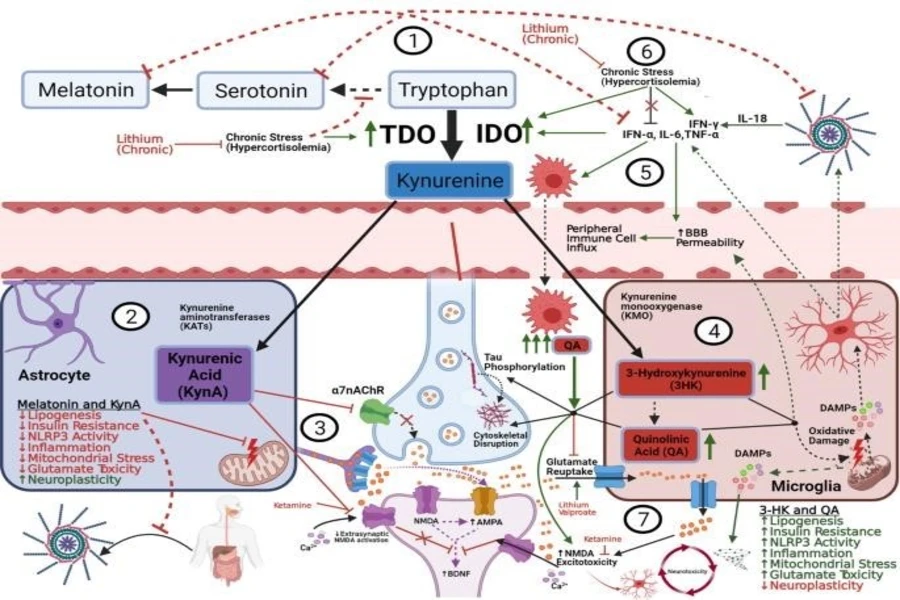
Bipolar disorder has been associated with dysregulation of the endocrine system, especially in the following: Hormonal Imbalance.
- Cortisol: Hypercortisolemia has been reported in bipolar disorder, especially during mania.
2 . Thyroid hormones: Individuals with bipolar disorder might also develop thyroid dysfunction that affects the stability of mood.
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal- Adrenal (HPA axis)
The HPA axis is important for the regulation of stress response and hormone secretion. Abnormality of the HPA axis has been implicated in bipolar disorder.
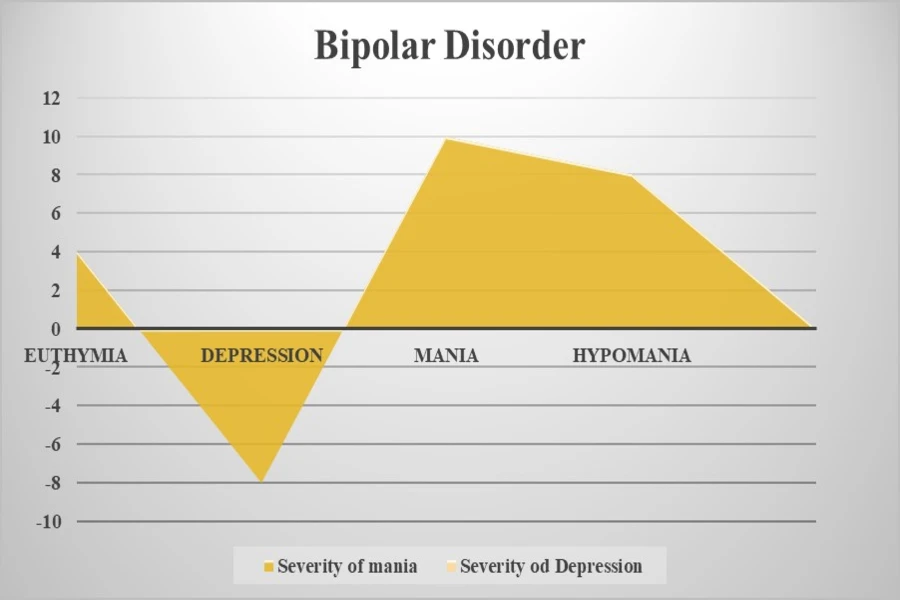
Illness trajectory in Bipolar Disorder
S.NO. | Patterns of trajectory | |
1. | Episodic | Characterized by distinct episodes of mania or depression, with periods of stability in between. |
2. | Chronic | Persistent symptoms with little or no periods of stability. |
3. | Cyclical | Regular cycles of mania and depression. |
4. | Mixed | Simultaneous symptoms of mania and depression. |
Symptoms
- Manic episodes: Elevated mood, excess energy, sleep reduction, impulsiveness, and reckless behaviour.
- Depressive episodes: Low mood, loss of interest in activities, appetite or sleep changes, fatigue, and feelings of worthlessness or guilt.
Treatment
- Medications: Mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, and antidepressants can be administered to treat symptoms.
- Therapy: Cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT), family therapy, and interpersonal therapy may assist in helping individuals deal with the condition.
Treatment of Bipolar Depression |
Medications:
|
Therapy:
|
Other:
|
Treatment of Mania and Hypomania |
Medications:
|
Therapy:
|
Other:
|
Precautions
- Exercise regularly, proper diet, and stress control can alleviate symptoms.
- Consult a mental health professional.
- Adhere to medications regimens.
- Maintain consistent sleep schedule.
Conclusion
Bipolar disorder is a recurrent mental illness that impacts moos, energy, and activity, resulting in wide mood swings between manic/hypomanic and depressive states. It needs to be treated comprehensively and monitored regularly to enable the individual to gain stability and enhance quality of life.
References:
FAQs
- What is bipolar disorder?
Bipolar Disorder is a Psychiatric condition that involves severe mood changes, from manic or hypomanic to depressive.
- What causes bipolar disorder?
The exact cause is unknown, but Biological factors, Environmental factors, Neurochemical factors can be responsible for bipolar disorder.
- What are the symptoms?
Manic episodes: elevated mood, increased energy
Depressive episodes: Low mood, loss of interest
- Can bipolar disorder be cured completely?
No, it can’t be cured completely, but symptoms can be managed with treatment and lifestyle changes.
- What precautions must be taken in bipolar condition?
Exercise regularly, proper diet, and stress control can alleviate symptoms.
Consult a mental health professional, Adhere to medications regimens. Maintain consistent sleep schedule.